File:Karmarkar.svg
From testwiki
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 720 × 540 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 240 pixels | 640 × 480 pixels | 1,024 × 768 pixels | 1,280 × 960 pixels | 2,560 × 1,920 pixels.
Original file (SVG file, nominally 720 × 540 pixels, file size: 43 KB)
This file is from Wikimedia Commons and may be used by other projects. The description on its file description page there is shown below.
Summary
| DescriptionKarmarkar.svg |
English: Solution of example LP in Karmarkar's algorithm.
Blue lines show the constraints, Red shows each iteration of the algorithm. |
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Gjacquenot |
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license:
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
Source code (Python)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# Python script to illustrate the convergence of Karmarkar's algorithm on
# a linear programming problem.
#
# http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karmarkar%27s_algorithm
#
# Karmarkar's algorithm is an algorithm introduced by Narendra Karmarkar in 1984
# for solving linear programming problems. It was the first reasonably efficient
# algorithm that solves these problems in polynomial time.
#
# Karmarkar's algorithm falls within the class of interior point methods: the
# current guess for the solution does not follow the boundary of the feasible
# set as in the simplex method, but it moves through the interior of the feasible
# region, improving the approximation of the optimal solution by a definite
# fraction with every iteration, and converging to an optimal solution with
# rational data.
#
# Guillaume Jacquenot
# 2015-05-03
# CC-BY-SA
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure, show, rc, grid
class ProblemInstance():
def __init__(self):
n = 2
m = 11
self.A = np.zeros((m,n))
self.B = np.zeros((m,1))
self.C = np.array([[1],[1]])
self.A[:,1] = 1
for i in range(11):
p = 0.1*i
self.A[i,0] = 2.0*p
self.B[i,0] = p*p + 1.0
class KarmarkarAlgorithm():
def __init__(self,A,B,C):
self.maxIterations = 100
self.A = np.copy(A)
self.B = np.copy(B)
self.C = np.copy(C)
self.n = len(C)
self.m = len(B)
self.AT = A.transpose()
self.XT = None
def isConvergeCriteronSatisfied(self, epsilon = 1e-8):
if np.size(self.XT,1)<2:
return False
if np.linalg.norm(self.XT[:,-1]-self.XT[:,-2],2) < epsilon:
return True
def solve(self, X0=None):
# No check is made for unbounded problem
if X0 is None:
X0 = np.zeros((self.n,1))
k = 0
X = np.copy(X0)
self.XT = np.copy(X0)
gamma = 0.5
for _ in range(self.maxIterations):
if self.isConvergeCriteronSatisfied():
break
V = self.B-np.dot(self.A,X)
VM2 = np.linalg.matrix_power(np.diagflat(V),-2)
hx = np.dot(np.linalg.matrix_power(np.dot(np.dot(self.AT,VM2),self.A),-1),self.C)
hv = -np.dot(self.A,hx)
coeff = np.infty
for p in range(self.m):
if hv[p,0]<0:
coeff = np.min((coeff,-V[p,0]/hv[p,0]))
alpha = gamma * coeff
X += alpha*hx
self.XT = np.concatenate((self.XT,X),axis=1)
def makePlot(self,outputFilename = r'Karmarkar.svg', xs=-0.05, xe=+1.05):
rc('grid', linewidth = 1, linestyle = '-', color = '#a0a0a0')
rc('xtick', labelsize = 15)
rc('ytick', labelsize = 15)
rc('font',**{'family':'serif','serif':['Palatino'],'size':15})
rc('text', usetex=True)
fig = figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([0.12, 0.12, 0.76, 0.76])
grid(True)
ylimMin = -0.05
ylimMax = +1.05
xsOri = xs
xeOri = xe
for i in range(np.size(self.A,0)):
xs = xsOri
xe = xeOri
a = -self.A[i,0]/self.A[i,1]
b = +self.B[i,0]/self.A[i,1]
ys = a*xs+b
ye = a*xe+b
if ys>ylimMax:
ys = ylimMax
xs = (ylimMax-b)/a
if ye<ylimMin:
ye = ylimMin
xe = (ylimMin-b)/a
ax.plot([xs,xe], [ys,ye], \
lw = 1, ls = '--', color = 'b')
ax.set_xlim((xs,xe))
ax.plot(self.XT[0,:], self.XT[1,:], \
lw = 1, ls = '-', color = 'r', marker = '.')
ax.plot(self.XT[0,-1], self.XT[1,-1], \
lw = 1, ls = '-', color = 'r', marker = 'o')
ax.set_xlim((ylimMin,ylimMax))
ax.set_ylim((ylimMin,ylimMax))
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlabel('$x_1$',rotation = 0)
ax.set_ylabel('$x_2$',rotation = 0)
ax.set_title(r'$\max x_1+x_2\textrm{ s.t. }2px_1+x_2\le p^2+1\textrm{, }\forall p \in [0.0,0.1,...,1.0]$',
fontsize=15)
fig.savefig(outputFilename)
fig.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = ProblemInstance()
k = KarmarkarAlgorithm(p.A,p.B,p.C)
k.solve(X0 = np.zeros((2,1)))
k.makePlot(outputFilename = r'Karmarkar.svg', xs=-0.05, xe=+1.05)
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
3 May 2015
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:34, 22 November 2017 | 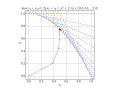 | 720 × 540 (43 KB) | wikimediacommons>DutchCanadian | The right hand side for the constraints appears to be p<sup>2</sup>+1, rather than p<sup>2</sup>, going by both the plot and the code (note the line <tt>self.B[i,0] = p*p + 1.0</tt>). Updated the header line. |
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file:
Retrieved from "https://en.beta.math.wmflabs.org/wiki/File:Karmarkar.svg"